Unlock the mystery behind Trichotillomania, a condition affecting millions worldwide. Imagine the constant urge to pull out your hair, an irresistible compulsion that can take control of your thoughts and actions. It’s a complex disorder with deep-rooted causes, but fear not!
In this blog post, we’ll explore the symptoms and impacts of Trichotillomania on daily life. We’ll also dive into practical treatments that can help you regain control over those impulsive hands.
Whether you’re seeking therapy options, medication alternatives, or natural remedies – we’ve got you covered! So please sit back, relax (but not too much), and unravel the secrets of overcoming Trichotillomania together!
Contents
- 1 What is Trichotillomania?
- 2 Symptoms and Causes
- 3 Impact on Daily Life
- 4 Common Treatments for Trichotillomania
- 5 Therapy Options: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and Habit Reversal Training
- 6 Medication Options
- 7 Natural Remedies
- 8 Support Groups and Resources for Trichotillomania
- 9 Coping Strategies for Managing Hair Pulling Urges
- 10 Conclusion
What is Trichotillomania?
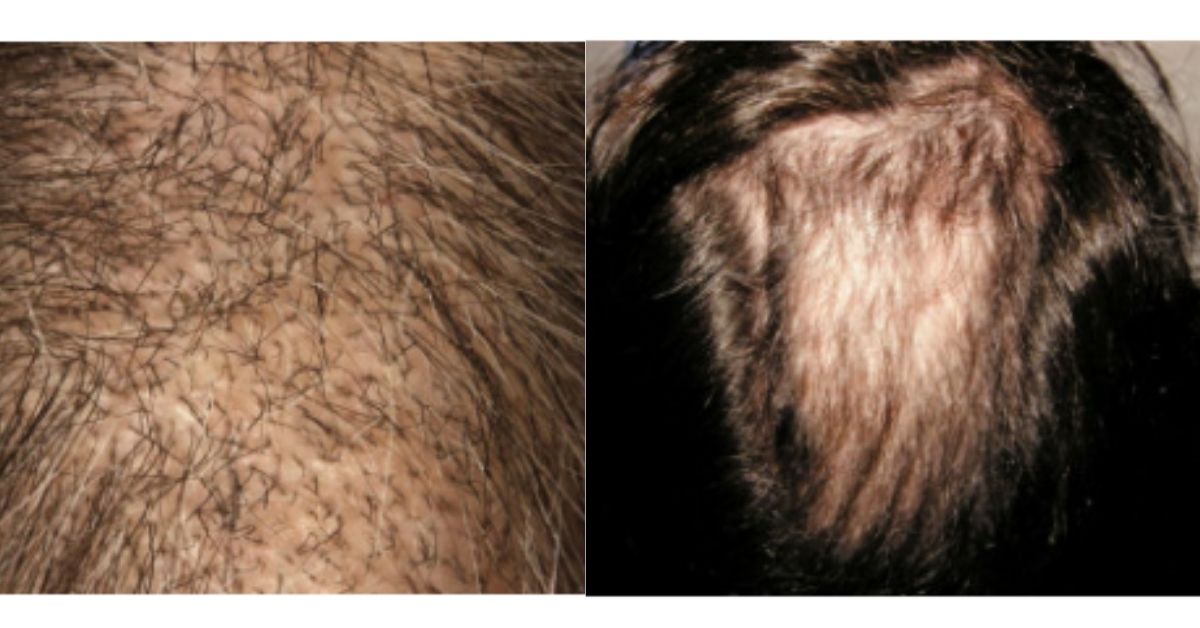
Trichotillomania, also known as hair-pulling disorder, is a psychological condition characterized by the irresistible urge to pull out one’s hair. While it may seem like an odd habit to some, for those living with Trichotillomania, it can be a distressing and frustrating experience.
The exact cause of Trichotillomania remains unknown. However, research suggests that it may be linked to various factors such as genetics, neurological imbalances, or even stress and anxiety. It often begins during adolescence but can continue into adulthood if left untreated.
Symptoms of Trichotillomania include recurrent hair pulling resulting in noticeable hair loss, tension or discomfort before pulling the hair, feelings of relief or pleasure after removing the hair, and significant impairment in social or occupational functioning.
This disorder can have a profound impact on daily life. Individuals with Trichotillomania may feel embarrassed or ashamed about their appearance due to bald patches or thinning hair. They might also avoid certain social situations that could expose their condition. Additionally, the constant preoccupation with thoughts of hair pulling can lead to decreased self-esteem and increased anxiety levels.
Understanding what Trichotillomania is just the first step towards finding effective treatments for this challenging condition. In the following sections of this blog post, we will explore different therapy options such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Habit Reversal Training (HRT), medication alternatives that have shown promise in managing symptoms of Trichotillomania_, natural remedies worth considering_, support groups available for individuals seeking connection with others facing similar challenges_, and coping strategies for managing those strong urges to pull out your precious locks_. So keep reading!
Symptoms and Causes
Trichotillomania, commonly referred to as hair-pulling disorder, is a multifaceted psychological ailment impacting millions of individuals globally. The symptoms of Trichotillomania can vary from person to person but typically involve the irresistible urge to pull out one’s hair. This often results in noticeable hair loss, bald patches, and distress.
Although the precise causes of trichotillomania are unknown, a mix of psychological, environmental, and genetic variables are thought to be involved.
Some individuals may have a family history of the disorder or other related conditions like obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) or anxiety disorders. Stressful life events or trauma can also contribute to the development of Trichotillomania.
Trichotillomaniacs frequently feel tense or anxious right before they remove their hair, and then they feel relieved or happy afterward.
It becomes a repetitive behavior that serves as a coping mechanism for emotional distress.
It’s important to note that Trichotillomania is not simply a bad habit or choice; it is a mental health condition that requires understanding and compassion. Seeking professional help from therapists specializing in treating this disorder can provide valuable support and guidance on effectively managing symptoms.
Remember: if you suspect you may have Trichotillomania or know someone who does, reaching out for help is crucial in finding appropriate treatment options tailored to individual needs.
Impact on Daily Life
Living with Trichotillomania can have a profound impact on one’s daily life. The constant urge to pull out hair can consume thoughts and actions, making focusing on work, school, or social activities difficult. It can lead to feelings of embarrassment and shame, causing individuals to withdraw from their usual routines and interactions.
The physical consequences of Trichotillomania are also significant. Bald patches and thinning hair can be noticeable to others, leading to self-consciousness and avoidance of social situations. Pulling out hair itself can cause pain or discomfort, further adding to the distress experienced by those with this condition.
Trichotillomania may also affect relationships as loved ones may struggle to understand the compulsion behind the behavior. This lack of understanding can strain friendships and family dynamics, leaving individuals feeling isolated and misunderstood.
Additionally, the emotional toll must be considered. Feelings of guilt, frustration, and helplessness often accompany Trichotillomania. These emotions may increase stress levels, exacerbating the urge for hair-pulling.
Managing Trichotillomania requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both the physical symptoms and the emotional aspects impacting an individual’s daily life.
Common Treatments for Trichotillomania
When treating Trichotillomania, various options can help individuals overcome the urge to pull out their hair. The most common treatments for this condition include therapy, medication, natural remedies, and support groups.
Therapy is often considered the first line of treatment for Trichotillomania. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Habit Reversal Training (HRT) are particularly effective in helping individuals manage their hair-pulling urges. CBT focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with hair pulling. HRT helps individuals develop alternative habits or responses when they feel the urge to pull.
In some cases, medication may be prescribed alongside therapy to help reduce symptoms of Trichotillomania. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), such as fluoxetine or sertraline, are commonly used antidepressants that have shown some effectiveness in reducing hair-pulling behaviors.
For those who prefer a more natural approach, several remedies may relieve trichotillomania symptoms. These include mindfulness techniques, relaxation exercises like deep breathing or yoga, keeping hands busy with fidget toys or stress balls, and using products like bitter-tasting nail polish to discourage hair pulling.
Support groups can also play a crucial role in the treatment process by providing a safe space for individuals with Trichotillomania to share their experiences and learn from others who face similar challenges.
Online resources and forums explicitly dedicated to Trichotillomania offer valuable information and opportunities for connecting with others who understand what you’re going through.
Remember that finding the right combination of treatments may take time and patience. It’s important not to give up hope if one method doesn’t work immediately – everyone’s journey towards recovery is unique! With dedication and a comprehensive approach, individuals with Trichotillomania can find practical.
Therapy Options: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and Habit Reversal Training
When it comes to treating Trichotillomania, therapy options can play a crucial role in helping individuals overcome the urge to pull their hair. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Habit Reversal Training (HRT) are two common therapeutic approaches for this condition.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy focuses on identifying and challenging the negative thoughts and beliefs contributing to hair pulling. Through CBT, individuals learn alternative coping strategies to manage stress or anxiety that may trigger their hair-pulling urges.
On the other hand, Habit Reversal Training aims to replace your pulling with healthier behaviors. This technique involves increasing awareness of when the urge arises and implementing a competing response, such as clenching fists or engaging in an activity that keeps hands busy.
Both CBT and HRT require active participation from the individual seeking treatment. Working closely with a trained therapist can provide guidance, support, and accountability.
It’s important to note that therapy is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Different techniques may work better for different people, so finding what resonates with you is critical. Some individuals may benefit from combining CBT and HRT, while others may succeed with just one approach.
Remember, therapy takes time and commitment. It’s a journey towards understanding oneself better and developing effective strategies for managing trichotillomania urges. If you’re considering therapy as part of your treatment plan, consult with a mental health professional who specializes in Trichotillomania or related disorders.
Stay tuned for our next blog post to explore medication options for treating Trichotillomania!
Medication Options
For individuals with Trichotillomania, medication can be an effective tool in managing the condition. While it’s important to note that medication alone may not completely stop hair pulling, it can help reduce symptoms and control urges.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly prescribed for trichotillomania treatment. These medications increase serotonin levels in the brain, which is thought to play a role in regulating mood and behavior. SSRIs such as fluoxetine (Prozac), sertraline (Zoloft), and escitalopram (Lexapro) have shown some success in reducing hair-pulling behaviors.
In addition to SSRIs, other medications like n-acetylcysteine (NAC) have also been explored as potential options for treating Trichotillomania. NAC is an antioxidant that has been found to modulate glutamate levels in the brain, potentially affecting compulsive behavior.
It’s worth noting that medication should always be prescribed and monitored by a qualified healthcare professional who specializes in mental health disorders. They will consider factors such as individual needs, medical history, and potential side effects when determining the appropriate course of treatment
While medication can offer relief for some individuals with Trichotillomania, it may not be suitable or necessary for everyone. It is essential to discuss all available options with your healthcare provider before making any decisions about your treatment plan.
Natural Remedies
When it comes to managing Trichotillomania, many individuals are seeking natural remedies as an alternative or complement to traditional treatments. While there is limited scientific research specifically on natural remedies for this condition, some people have reported finding relief through various approaches. Here are a few potential options worth exploring:
- Aromatherapy: Essential oils like lavender and chamomile can be used in diffusers or applied topically to promote relaxation and reduce anxiety, potentially helping to curb the urge to pull hair.
- Herbal supplements: Certain herbs, such as passionflower and valerian root, help alleviate stress and improve overall well-being, which could indirectly impact hair-pulling behaviors.
- Mindfulness techniques: Practices like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can enhance self-awareness and promote emotional regulation, potentially reducing the frequency of hair-pulling episodes.
- Healthy lifestyle habits: Regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet rich in nutrients (such as omega-3 fatty acids), getting enough sleep, and minimizing caffeine intake may contribute to better overall mental health.
It’s important to note that these natural remedies should not replace professional treatment but rather be used as adjunctive strategies. It’s always best to consult a healthcare provider before incorporating new approaches into your treatment plan.
Remember that what works for one person may not work for another when managing trichotillomania symptoms. Therefore, finding the right combination of therapies that work best for you is essential.
Support Groups and Resources for Trichotillomania
Finding support and resources can be crucial in managing Trichotillomania. Connecting with others who understand your struggles can provide a sense of community and validation. Support groups offer a safe space to share experiences, exchange coping strategies, and gain encouragement from individuals who are going through similar challenges.
Online forums and social media platforms have become famous avenues for those seeking virtual support. Websites like the Trichotillomania Learning Center (TLC) provide online communities where people can connect with others facing hair-pulling disorders. These platforms allow individuals to share their stories, ask questions, receive empathetic responses, and access valuable educational resources.
In-person support groups also exist in many communities around the world. These meetings typically involve facilitated discussions or group therapy sessions led by trained professionals or peers who have firsthand experience with Trichotillomania. Attending these gatherings can foster a sense of belonging while offering practical tips on managing urges to pull hair.
Additionally, therapists specializing in trichotillomania treatment can be an invaluable resource. They possess expertise in understanding the disorder’s psychological aspects and providing tailored interventions to help individuals overcome compulsive hair-pulling behaviors.
Furthermore, various self-help books written explicitly for Trichotillomania offer guidance on techniques like habit reversal training (HRT), cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), mindfulness exercises, relaxation techniques, etc.
Everyone’s journey is unique; what works for one person may not work for another. Exploring different support options allows you to find what resonates best with you.
Coping Strategies for Managing Hair Pulling Urges
Finding effective coping strategies can be crucial in managing and reducing the urge to pull hair. While everyone’s experience with Trichotillomania is unique, here are a few strategies that may help:
- Awareness and mindfulness: Developing self-awareness is an essential first step. Pay attention to triggers or situations that lead to hair-pulling urges. Mindfulness techniques such as deep breathing and meditation can also help redirect focus away from the urge.
- Substitute behaviors: Engaging in alternative activities can distract from the urge to pull hair. Some people find keeping their hands busy with objects like stress balls or fidget toys helpful.
- Habit reversal training (HRT): HRT involves identifying patterns of hair pulling and replacing them with more positive behaviors, such as clenching fists or holding onto something.
- Support system: Reach out to friends, family, or support groups who understand your struggle and offer encouragement during difficult times.
- Self-care routine: Prioritize self-care activities like exercise, proper sleep, healthy eating, and relaxation techniques to reduce stress levels.
Remember that finding effective coping mechanisms may require trial and error, as what works for one person may not work for another.
By incorporating these strategies into your daily life while seeking professional help when needed, you can take control of trichotillomania urges and begin on a path toward recovery.
Conclusion
Trichotillomania is a challenging disorder that can have a significant impact on a person’s daily life. However, effective treatments are available to help manage and reduce hair-pulling behaviors.
Therapy options such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Habit Reversal Training (HRT) have shown promise in helping individuals gain control over their urges to pull out their hair. These therapies focus on identifying triggers, developing coping mechanisms, and changing negative thought patterns associated with the behavior.
Medication options may also be considered for those who require additional support. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), N-acetylcysteine, or other medications prescribed by healthcare professionals can help alleviate symptoms of anxiety or depression that often accompany Trichotillomania.
Natural remedies like keeping hands busy with fidget toys or stress balls, practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises or meditation, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and sufficient sleep, can complement other treatments.
Support groups and resources specifically tailored for individuals with Trichotillomania can provide valuable emotional support and practical tips for managing the condition. Connecting with others who understand firsthand what it’s like to live with this disorder can be empowering.
Implementing coping strategies such as wearing hats or scarves to prevent access to hair-pulling sites, using barrier methods like gloves or bandages on fingertips when necessary, and setting achievable goals for reducing hair-pulling episodes gradually – all these strategies contribute towards managing the urge more effectively.
Remember that overcoming Trichotillomania takes time and patience. Working closely with qualified professionals who specialize in treating this disorder is essential while building a solid support system around you.
With consistent effort and appropriate interventions in place, it is possible to regain control over your life and minimize the impact of Trichotillomania on your well-being!